2 Popular Foods May Turn Immune System Against Brain
Written By Sayer Ji, Founder
Two of the Western world’s most popular foods have been implicated in immune mediated brain damage.
A study published in the open access journal Nutrients titled, “The Prevalence of Antibodies against Wheat and Milk Proteins in Blood Donors and Their Contribution to Neuroimmune Reactivities,” implicates two of the Western world’s most popular foods in various forms of immune-mediated brain damage and dysfunction, including gluten ataxia and multiple sclerosis.
A group of U.S. researchers set out to ascertain the presence of IgG, IgM, and IgA antibodies against wheat and milk, in 400 blood samples, from 181 males and 219 female donors of mixed ancestry. Because wheat and milk antibodies have been found in elevated concentrations in various neuroimmune disorders, the researchers measured the co-occurrence of their antibodies against the following brain proteins:
- GAD-65 (Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase)
- Cerebellar peptides
- MBP (myelin basic protein)
- MOG (myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein)
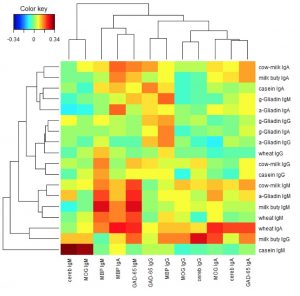
Their results revealed significant clustering when certain wheat and milk protein antibodies were cross-referenced with neural antibodies.
[Figure 8. Two-way cluster analysis of the Pearson’s correlation coefficients between the food proteins and the brain proteins.]
While not a direct causal link, these associations do signal a very real possibility that the increase in antibody titers against food antigens can cause cross-reactivity to brain proteins through a process known as molecular mimicry, presumably resulting in neurological damage.
The results were reported in the study abstract as follows:
“Approximately half of the sera with antibody elevation against gliadin reacted significantly with GAD-65 and cerebellar peptides; about half of the sera with elevated antibodies against α + β-casein and milk butyrophilin also showed antibody elevation against MBP and MOG.”
Based on these results they arrived at the following conclusion:
“We conclude that a subgroup of blood donors, due to a breakdown in immunological tolerance, may react and produce significant levels of antibodies (p-values less than 0.05) against wheat and milk antigens that cross-react with different neural antigens, which may have broader implications in the induction of neuroimmune reactivities.”
How Wheat Opens Pandora’s Box
One might wonder how the ingestion of seemingly common and innocuous foods can result in a condition as serious as the immune system attacking the human brain. The fact is that available scientific research already clearly reveals how such a grave consequence can (and does) emerge. Modern bread wheat, for instance, contains over 23,000 distinct proteins, some of which are capable of up-regulating intestinal permeability in the guts of susceptible individuals, e.g. alpha gliadin, and a lectin (carbohydrate-binding protein) known as wheat germ agglutinin also capable of penetrating the intestinal lining. This results in the entry of a wide range of antigenic proteins and intestinal contents (e.g. bacteria) into the blood stream – any number of which contribute to inappropriate immune reactions, systemic inflammation, and ultimately the loss of immunological self-tolerance.
 Of course, this does not happen to everyone who consumes wheat because there so many contributing variables involved. Indeed, the researchers noted that the observed relationship between food antigens and cross-reactive antibodies to neural proteins is complex and that “multiple factors, including an individual’s genotype, the timing and level of exposure, and the health of the gut and blood brain barriers,” are involved and which need further study.
Of course, this does not happen to everyone who consumes wheat because there so many contributing variables involved. Indeed, the researchers noted that the observed relationship between food antigens and cross-reactive antibodies to neural proteins is complex and that “multiple factors, including an individual’s genotype, the timing and level of exposure, and the health of the gut and blood brain barriers,” are involved and which need further study.
Extensive Body of Research Linking Wheat to Brain Damage
While the concept that common food proteins can cause the immune system to attack the brain may be surprising to many who still consider cow’s milk and wheat-based products to be ‘wholesome,’ this is not a novel finding. There is already a sizable body of literature implicating these two foods in a wide range of neurological problems. Wheat’s intrinsic neurotoxicity has been a large focus of our previous research; a link which we covered in depth in the following articles:
- The Grain That Damages The Human Brain
- Wheat Drives More Than Your Digestive System Crazy
- 60 Years of Research Links Gluten Grains to Schizophrenia
There is also the related fact that of the 200+ adverse health effects linked to gluten-containing grains we have identified in the biomedical literature, neurotoxicity is top on the list of the 21 distinct modes of toxicity we have identified thus far.[i]
With best selling books like Dr. William Davis’ Wheat Belly and Dr. David Perlmutter’s Grain Brain opening so many minds to the value of a grain- and wheat-free diet, there is now a compelling intellectual context for understanding why the burgeoning gluten free industry is not based on a ‘diet fad.’ But what about cow’s milk?
Cow’s Milk and Immune and Nervous System Dysfunction
While cow’s milk has been linked to over 50 adverse health effects in the biomedical literature, few consider it a risk for immune related neurological problems. And yet, this latest study is not the first of its kind to identify possible adverse effects of cow’s milk consumption on the immune and central nervous systems.
It is already well known that cow’s milk consumption increases the risk of type 1 diabetes, which involves the autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. There is also recent research showing that Drinking Cow’s Milk During Breastfeeding Increases Risk of Baby’s Allergies, indicating another immune disrupting property of milk. These adverse immunological consequences of cow’s milk consumption only scratch the surface of the problem. And while raw, pasture raised, non-homogenized, organic milk is definitely superior to conventional, the health issues associated with its consumption may be insurmountable because it is an evolutionarily incompatible ‘food.’ Molecular evidence now exists showing how milk (and wheat) proteins can contribute to turning the host immune system against its own brain through the phenomena of molecular mimicry. This is a truly frightening prospect, and likely one that affects millions of milk consumers, even if mostly subclinically.
A 2000 study found that one key mechanism behind the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis is the production of antibodies to a protein in cow’s milk known as butyrophilin that cross-react to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein, a major component of the central nervous system.[i] Additionally, a 2004 study found patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) had highly significant elevations for IgA antibodies against another milk protein known as casein versus controls.[ii] This cow’s milk protein (butrophilin) linked cross-reactivity has also been identified in autistic patients.[iii] Another 2008 study found that a milk-free diet downregulates folate receptor autoimmunity in cerebral folate deficiency syndrome, a condition which involves decreased folate transport to the central nervous system.[iv]
Clearly, given the evidence for the potential of milk and wheat to incite autoimmunity and/or neurological damage, anyone who suffers from a neurological or immune condition should consider at the very least getting tested for autoantibodies to these food antigens. Or, opting for a less clinical approach, one can simply eliminate the foods in question in order to ascertain through direct experience if there is a noticeable improvement.
References
[i] A Stefferl, A Schubart, M Storch2, A Amini, I Mather, H Lassmann, C Linington. Butyrophilin, a milk protein, modulates the encephalitogenic T cell response to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2000 Sep 1;165(5):2859-65. PMID: 10946319
[ii] K-L Reichelt, D Jensen. IgA antibodies against gliadin and gluten in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 2004 Oct;110(4):239-41. PMID: 15355487
[iii] A Vojdani, A W Campbell, E Anyanwu, A Kashanian, K Bock, E Vojdani. Antibodies to neuron-specific antigens in children with autism: possible cross-reaction with encephalitogenic proteins from milk, Chlamydia pneumoniae and Streptococcus group A. J Neuroimmunol. 2002 Aug;129(1-2):168-77. PMID: 12161033
[iv] Vincent T Ramaekers, Jeffrey M Sequeira, Nenad Blau, Edward V Quadros. A milk-free diet downregulates folate receptor autoimmunity in cerebral folate deficiency syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2008 May ;50(5):346-52. Epub 2008 Mar 19. PMID: 18355335
 Sayer Ji is founder of Greenmedinfo.com, a reviewer at the International Journal of Human Nutrition and Functional Medicine, Co-founder and CEO of Systome Biomed, Vice Chairman of the Board of the National Health Federation, Steering Committee Member of the Global Non-GMO Foundation.
Sayer Ji is founder of Greenmedinfo.com, a reviewer at the International Journal of Human Nutrition and Functional Medicine, Co-founder and CEO of Systome Biomed, Vice Chairman of the Board of the National Health Federation, Steering Committee Member of the Global Non-GMO Foundation.
Disclaimer: This article is not intended to provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Views expressed here do not necessarily reflect those of GreenMedInfo or its staff. This article is copyrighted by GreenMedInfo LLC, 2019