Why this sudden flurry of activity? The new satellite fleets are contributing to a concerted global effort to ‘upgrade’ the electromagnetic environment of the Earth. The upgrade is commonly referred to as 5G, or fifth generation wireless network. It has become customary in tech circles to talk about the introduction of 5G as involving the creation of a new global “electronic ecosystem.” It amounts to geo-engineering on a scale never before attempted. While this is being sold to the public as an enhancement of the quality of video streaming for media and entertainment, what is really driving it is the creation of the conditions within which electronic or “artificial” intelligence will be able to assume an ever-greater presence in our lives.
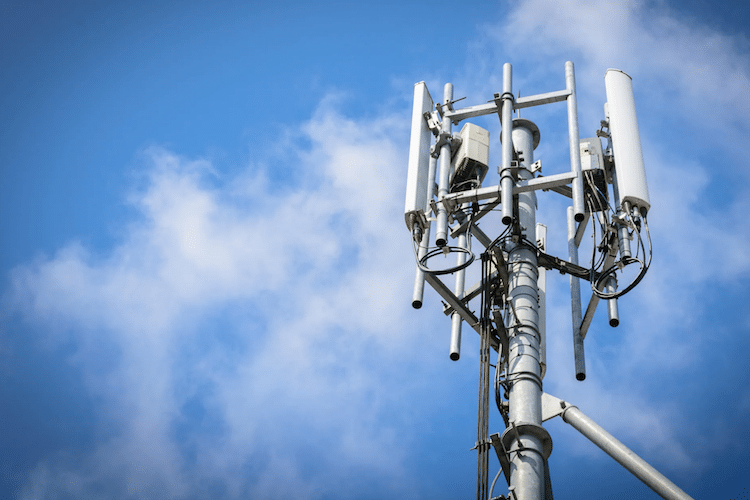
The introduction of 5G will also require hundreds of thousands of new mini mobile phone masts (also referred to as “micro-cells” or “base stations”) in urban centres throughout Australia, and literally millions of new masts in cities throughout the rest of the world, all emitting radiation at frequencies and at power levels far higher than those to which we are presently subjected. These new masts are much smaller than the masts we currently see beside highways and on top of buildings. They will be discreetly attached to the side of shops and offices or secured to lampposts. The 20,000 satellites are a necessary supplement to this land-based effort, for they will guarantee that rural areas, lakes, mountains, forests, oceans and wildernesses, where there are neither buildings nor lampposts, will all be incorporated into the new electronic infrastructure. Not one inch of the globe will be free of radiation.
Given the scale of the project, it is surprising how few people are aware of the enormity of what is now just beginning to unfold all around us. Very few people have even heard about the 20,000 new satellites that are due to transform the planet into a so-called “smart planet,” irradiating us night and day. In the national media, we do not hear voices questioning the wisdom, let alone the ethics, of geo-engineering a new global electromagnetic environment. Instead, there is a blithe acceptance that technology must continue to progress, and the presence in our lives of increasingly “smart” machines and gadgets that each year become cleverer and more capable is an inevitable part of this progress. And who doesn’t want progress? Almost everyoneloves their sleek and seductively designed phones, iPads and virtual assistants, and regards them as an indispensable part of their lives.
The question we should ask is whether we also want increasingly intense exposure of the natural environment and all living creatures, including ourselves, to more and more electromagnetic radiation. Is it likely that this does not entail any adverse health consequences, as both government and industry claim? If the electromagnetic waves that connect our smartphones to the Internet travel through brick, stone and cement, then what happens when these same waves encounter our bodies? Be assured that they do not just bounce off us! They travel into the human body. The degree to which they are absorbed can be precisely measured in what is called the Specific Absorption Rate, expressed in Watts per kilogram of biological tissue. When we fill our houses with WiFi, we are irradiating our bodies continuously. When we hold a smartphone to our ear, electromagnetic waves irradiate our brains. Do we really believe this could be completely harmless?
Waves and Frequencies At present, mobile phones, smartphones, tablets, WiFi and so on all operate at under 3 GHz in what is called the “microwave” region of the electromagnetic spectrum. If you could see and measure their wavelengths, you would find that they are many centimeters (or inches) long. A smartphone operating at 800 MHz, for example, sends and receives signals with wavelengths of 37.5 centimeters (just under 15 inches). Operating at 1.9 GHz, the wavelengths are 16 centimeters (just over 6 inches). WiFi uses the 2.4 GHz frequency band with 12 centimeter wavelengths (just under 5 inches long).
The introduction of 5G will entail the use of considerably higher frequencies than these, with correspondingly shorter wavelengths. Above 30 GHz, wavelengths are just millimeters rather than centimeters long. The millimeter waveband (from 30 GHz to 300 GHz) is referred to as Extremely High Frequency, and its wavelengths are between 10 millimeters and 1 millimeter in length.3 Up to the present time, Extremely High Frequency electromagnetic radiation has not been widely propagated, and its introduction marks a significant step change in the kind of electromagnetic energy that will become present in the natural environment.
The reason why millimeter waves are to be used for 5G is that much larger bands of spectrum are available in the Extremely High Frequencies than at lower frequencies. This means that there can be much broader “bandwidth.” Broader bandwidth means that larger quantities of data can be transferred and the speed of transfer of the data will be significantly faster. One of the effects of this is that it reduces what is called “latency,” or time-lag, in the system, improving the quality of video streaming. But in so doing, it also enables a greater seamlessness between the data accessible from virtual sources and our perceptions of objects in the real world, as is required, for example, in Augmented Reality applications. Greater seamlessness means that we more effortlessly inhabit the natural and the electronic worlds as if they were a single reality.
One of the technical problems of using frequencies in the millimeter region of the spectrum is that because the waves carrying the data are so tiny, being only millimeters long, they are less able to pass through physical barriers, like walls and trees, than are the longer waves of lower frequencies. This is why it is necessary to have so many more new “micro-cells” or “base stations.” They will need to be spaced at 100 meters apart in cities because beyond this distance their signals weaken and are therefore less able to penetrate buildings and connect with the devices inside. As well as being more closely spaced, the 5G micro-cells will operate at much higher power than current phone masts in order to ensure that the signals are sufficiently strong.
Because the wavelengths are so much smaller, the antennas transmitting and receiving them will also be much smaller than those of current phone masts and electronic devices. A single 5G transmitter/receiver will have a large number of tiny antennas, grouped together in one unit. An array of just over a thousand such antennas measures only four square inches, so will easily fit into a small base station on a lamppost, while the smartphone in your pocket will probably have sixteen.
Both 5G satellites and 5G land-based masts will use a system called the “phased array.” In phased array, groups of antennas are coordinated to radiate pulses in a specific direction and in a specified time sequence. This allows a concentrated beam of radio waves to be exactly aimed at designated targets, to enable signals to be sent or received. Because the beams are concentrated in this way, this adds to their power, which means they are able more easily to penetrate buildings. But it also means that any living creature that gets in the way of such a concentrated beam will be subjected to a powerful dose of extremely high frequency radiant electricity.
A study published earlier this year demonstrated that certain insects, because of their small body-size, are particularly vulnerable to the millimeter waves of the higher frequencies to be utilized by 5G.5 Other studies have shown that bacteria and plants are vulnerable, and so also (as one might expect) are the skin and the eyes of animals including, of course, human beings.6
As well as its ability to concentrate power in focused beams, phased array technology has a further complicating factor. Either side of the main beam, the time intervals between the pulses are different from the time intervals between those of the main beam, but they may overlap each other in such a way as to produce extremely rapid changes in the electromagnetic field. This can have a particularly detrimental effect on living organisms, because instead of the radiation decaying when it is absorbed into living tissue, it can be re-radiated within the body. The moving charges streaming into the body effectively become antennas that re-radiate the electromagnetic field and send it deeper into the organism. These re-radiated waves are known as Brillouin precursors, named after the French physicist Leon Brillouin, who first described them in 1914. Research suggests that they can have a significant and highly detrimental impact on living cells.8
The UN-reassuring Assurances of Government and Industry The government body charged with advising on the health effects of electromagnetic radiation, the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency (ARPANSA), seeks to reassure us that there is no established evidence that Radio Frequency radiation (which radio, television, mobile phones, smartphones and 5G all use) has any adverse health effects on either adults or children.9 ARPANSA’s advice is largely based on findings derived from the supposedly independent AGNIR (Advisory Group on Non-Ionising Radiation), which advises the UK Health Department.10 AGNIR’s report, published in 2012, on the safety of Radio Frequency radiation stated that there was a lack of “convincing” and “conclusive” evidence for any adverse health effects. It was like giving a blank cheque to the telecommunications industry to move into the higher frequencies without any heed for the consequences.11
It turns out that far from being independent, AGNIR has a high proportion of members with blatant conflicts of interests, and their report distorted or simply left out of account evidence that should have compelled them to reach the opposite conclusion to the one they arrived at. In a forensic analysis of the report, the environmental health researcher Sarah Starkey makes it clear that only a wilful disregard of the available scientific evidence could explain its internal contradictions and apparent incompetence.12 Yet it is, it seems, not only the basis of current UK government policy but also Australian government policy, allowing the roll out of 5G without so much as even a nod towards the need for a prior health and safety assessment.13 Health and safety simply do not feature in government thinking, despite a veritable mountain of literally thousands of research papers demonstrating adverse health effects which continues to grow at the rate of roughly 350 per year, on average practically one every day.14
One of the reasons for ignoring this evidence in the hell-for-leather dash to create the 5G electronic ecosystem is the conviction in government circles that unless we introduce it immediately, we will be “left behind” and our economic growth and competitiveness will be put at risk. There is simply no time to consider the possible health consequences. The rewards of the “connected future” are to be measured in billions of dollars worth of revenue. The mind-boggling amounts involved are well exemplified in a recent estimate that the global media industry alone stands to gain $1.3 trillion from 5G by 2025, not least because 5G will “unlock the potential of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR).”15 The irony that the “connected” future is one in which dizzying profits stand to be made from technologies that disconnect us more and more from the real world is entirely missed.
The sums involved are sufficient to explain why the telecom industry has for the last 25 years done its utmost to ensure that research into the health effects of wireless technologies produce negative or inconclusive results. Since 1993, the industry has financed a large number of studies, saving governments a great deal of expense and at the same time preserving the convenient illusion that the jury is still out on whether exposure to Radio Frequency radiation causes harm.
Earlier this year, The Guardian published an article citing research which showed that while 67% of independently funded studies found a biological effect of exposure to Radio Frequency radiation, only 28% of industry-funded studies did. Industry-funded studies are almost two and a half times less likely than independent studies to find health effects.16 The authors of the Guardian article explain that the telecom industry doesn’t need to win the scientific argument about safety, but simply keep the argument running indefinitely by producing studies with results that fail to verify, or even better contradict, the research that does find adverse health effects.
One of the most notorious is the mammoth, industry-funded “Inter-phone Study,” which managed to conclude that holding a mobile phone to the head actually protects the user from brain tumors! This study, which is full of contradictions and suffers from grievous design flaws, is often quoted as the most authoritative to date, while it has in fact been thoroughly discredited.17 Nevertheless, the impression is maintained that there is no scientific consensus, and so there are not sufficient grounds for action to be taken. Needless to say, this suits government just as much as it suits industry.
The Path to Total Immersion Beyond the health effects there is another level altogether of what the roll out of 5G actually entails. To gain a perspective on this, we should remember that it was not so long ago that the Earth’s electromagnetic field was undisturbed by human-generated electromagnetic frequencies. Before the 1880s, there were only two main causes of electromagnetism, both of them natural: the lightning of thunderstorms, which also set in motion the very weak, low frequency resonances known as Schumann Resonances, and sunlight. Lightning and sunlight produce effects in specific, and very limited, parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. The very idea that such a thing as “electromagnetism” and an “electromagnetic spectrum” existed was not even entertained before the nineteenth century. And, from the point of view of the pre-electrical age, the truth of the situation was that they indeed did not exist as a factor of experience. Beyond lightning and sunlight, the energies of the electromagnetic spectrum did not impact on human life, for they were entirely dormant.
In that pre-electrical world, both lightning and sunlight were regarded with a certain degree of awe, as natural phenomena expressive of powers greater than anything human beings could muster. In antiquity both were associated with gods – lightning with violent storm gods invariably with Underworld associations, like Seth, Baal and Zeus; and sunlight with sublime solar deities like Ra, Shamash and Apollo. In the later Judaeo-Christian era, the widespread sense that these phenomena had a spiritual source persisted, with lightning regarded as expressive of the divine wrath, and light as the garment of the cosmic Logos. We touch here a deeply felt relationship to nature that has been largely eroded in the centuries since the Scientific Revolution. In the course of the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, both lightning and light were stripped of their spiritual luminosity, clearing the way for an entirely materialistic explanation of light, and an entirely technological approach to electricity.
In the early days, the frequencies utilized were at the lower end of the electromagnetic spectrum. In the 1890s, the power lines that delivered the new mains electricity to factories and houses were standardized at either 50 or 60 Hz (or cycles per second). When public radio broadcasts began in the 1920s, they were mostly in the long-wave frequencies under 500 KHz (thousands of cycles per second). As the century wore on, the frequencies used by new and improved technologies became higher and higher. In the 1930s and ‘40s, medium and shortwave frequencies (between 500 KHz and 1700 KHz) were utilized, while in the 1950s the Very High Frequencies (VHF) of 30 – 300 MHz (or millions of cycles per second) were employed for both radio and TV broadcasting.
During World War II, a method was discovered for generating even higher frequencies, between 3 and 30 GHz (thousands of millions of cycles per second), which became the basis for radar. With each escalation in frequency, more power was required to transmit the radio waves. The advent of mobile phones, smartphones and WiFi, brought into widespread use the Ultra High Frequency (UHF) part of the spectrum (300 MHz – 3 GHz) for signal transmission. Transmission in these frequencies demands more than ten times the power needed for VHF transmission.
Today, poised at the threshold of the new era of an Extremely High Frequency “electronic ecosystem,” with frequencies of up to 70 GHz envisaged, yet more power will be required for effective transmission of its millimeter waves.18 Then the natural environment will be fully saturated with an invisible fog of radiation.
In this brief historical sketch, we see higher and higher frequencies forming the basis of each new technological innovation. As each one of the new technologies was introduced, human beings became a little more disassociated from the natural world. Consider how this happened. From the 1890s onward, the supply of mains electricity to homes, schools, hospitals and factories caused a revolution in living standards, liberating humanity from subservience to nature’s cycles of day and night, summer and winter, by giving access to a new source of light, warmth and power. Then, in the 1920s, radio enabled people to communicate over vast distances, and brought the voices of kings and politicians, singers and poets into our living rooms, even though they were not physically present.
In the 1950s, television intensified the experience of an absent yet present world, conveyed by the moving image. I remember as a child the addictive quality of television: one is drawn out of oneself and away from awareness of one’s immediate surroundings into the fascinating world of images on the screen.
With the advent of the smartphone, the trend towards addiction was greatly strengthened, partly because the screen became a portable interface with the Internet, and partly because of the deliberately exploitative policies of Facebook, Google and others to hook people into an addictive relationship with their devices.19 Smartphone addiction both dislocates users from their own inner center of stillness, and at the same time disconnects them from the natural environment.
5G will further accentuate this tendency for people to lose themselves, and it will weaken even more their relationship to nature, for it promises to make advanced immersive Virtual Reality accessible to all. While VR headsets have been commercially available for some time now, VR is still in its infancy. The next development in VR technology is to supplement the headset with a “haptic suit,” which enables the wearer to experience sensations of touch – pressure, warmth, hardness, softness, moisture and dryness – in virtual reality. Such opportunities for “total immersion” in virtual reality will lead to an increasing confusion as to which world we really belong: the electronically generated or the natural world. The use of Augmented Reality, made possible through special helmets, electronic glasses, or contact lenses, that overlay virtual content onto the experience of the physical world, will add to the confusion, as the virtual is increasingly integrated within the real world.20
People will become adjusted to regarding the virtual world as having as great a claim on their attention, their emotions and thoughts, as the natural world. The temptation will be to give their loyalty to that which not only undermines their relatedness to nature but also, through its assault on the imagination, has a corrosive effect on the inner life of the soul. The confusion will only be exacerbated by a huge increase in the use of 3D holographics that will give virtual entities the ability to incarnate electronically in the physical environment. This is what the saturation of the world with extremely high frequency millimeter waves will enable. The waves themselves are only part of the issue: it is the technologies that ride on the backs of the waves, and their impact on our inner life, that should also concern us.
The Formation of the Global Electronic Brain But if 5G promises to radically alter the experiential world we inhabit in these ways, there is something further that we must understand if we are to grasp what is really being prepared. At the same time as increasingly sophisticated technologies increasingly disconnect human beings from the natural world, a network of electronic “intelligence,” global in extent, gradually emerged. At first it was under close human supervision, but it has steadily grown more autonomous. Consider the difference between radio broadcasting and the Internet: the former is under tight human control and serves a very specific purpose, whereas the latter has established itself as a permanent, constantly available electronic infrastructure of undefined scope and reach. What has been happening over recent decades is the increasing co-ordination of intelligence-endowed machines, so that they operate without need of human supervision.
The efforts now underway to create a 5G electronic ecosystem are the necessary precondition for developing and perfecting a global Artificial Intelligence network which feeds on the very fast transfer of large amounts of information. This global electronic “brain,” innocuously called the “Internet of Things,” is already impacting on our lives.
Through the Internet of Things, more and more things will be linked to the Internet and made “smart” by being given the ability to function autonomously. On smart motorways your car will drive itself while you, wearing your VR headset and haptic vest, play interactive computer games in the back seat; and in your smart house your fridge will autonomously order more eggs, milk and cheese for you via a wireless connection with a supplier.
But the reality is that the Internet of Things is itself the precursor to what has been called the “Internet of Thinking,” in which human beings will find themselves having to live in relationship to the vast global electronic intelligence. It will be active everywhere in our environment and we shall be obliged to interact with it in order to accomplish the simplest of tasks.21 In the Internet of Thinking it is not hard to see the lineaments of an electronically supercharged totalitarian state, with unprecedented control over the minutiae of individuals’ lives. The possibility of this happening will only be increased by the thousands of new mini phone masts and satellites irradiating every inch of the planet with millimeter waves. For this is what 5G means: it means putting in place not just an improved telecommunications system, but rather a new “system of systems” – the infrastructure of electronic totalitarianism.22
A Curtain Drawn Against the Light As our world is increasingly smothered by a fog of radio waves, microwaves and millimeter waves, it may seem that the gods of the Underworld have taken hold of humanity in an ever-tightening grip, drawing us towards the false lights – the illusory lights of the hell-beings and hungry ghosts that the Tibetan Book of the Dead long ago warned against. The electromagnetic energies that we have summoned, and which promised to give us new powers, now appear to be overpowering us , carrying us down into an Underworld realm of hellish entertainment and distraction, of illusion and disconnection from the reality that really matters – the reality of nature and the spiritual order that infuses nature, the reality of fellow creatures with whom we share our world, living in soil and sky and walking the Earth beside us.
We must ask: Does the Earth need an electronic ecosystem? Is it going to benefit in any way from being irradiated with millimeter waves? Is there actually any need at all for 5G? Can we even remotely conceive that 5G is the answer to any of the pressing ecological, social and spiritual problems that face us today? We stand at a dreadful threshold, and yet surrender to despair cannot be the right response. What can we do?
First of all, we can protest! There are campaigns against 5G that we can join, there are petitions to sign, letters to write, and legal actions to support. The best place to begin is the “International Appeal to Stop 5G on Earth and in Space,” which has now gathered over 40,000 signatures, including those of many health professionals, environmentalists and other scientists.23 But as well as protest there is something further that needs to be done, and that is to bring spiritually informed understanding to the deeper significance of the global electronic brain whose emergence 5G will hasten.
To this end, we need to develop a clear perception of the moral quality of electricity, and to recognize the kind of spiritual entity or entities that it serves. This will empower us to break the spell that electricity and electronic technologies have cast over us, and enable us to form a more appropriate relationship to them. One of Rudolf Steiner’s most helpful insights into electricity was his observation that it is light in a fallen, degraded state – light that has fallen beneath nature into the sub-natural realm – and that is why we must actively guard against an ever-increasing dependence on it, for it threatens to drag us down.24
This points to a third thing we can do, which is really the foundation of everything else. It is to rebuild our relationship to the light, which in its selfless benevolence and purity greets us every morning, and which, unlike the false and illusory electronic lights that would lead us into the Underworld, beckons us in a quite different direction, towards our essential humanity.
Through a deepened meditative relationship to the light, practiced through the hours of the day and the seasons of the year, we can nurture a relationship to the inner light that is the source of all that is creative and good in the world. This inner light the Christian tradition knows as the cosmic Logos.
As the curtain of electro-smog is drawn across our world, we are presented with a sacred task that, come what may, we attend to all that the light has to give, for therein lies the divine Saving Power.
About the Author Jeremy Naydle r is a philosopher, cultural historian and gardener who lives and works in Oxford, England. He is author of several books on the history of consciousness, and has a longstanding concern about the impact of electronic technologies on our inner life and on our relationship to nature. His most recent publication is In the Shadow of the Machine: The Prehistory of the Computer and the Evolution of Consciousness (Forest Row: Temple Lodge, 2018).
Footnotes:
One of the best sources for this information is the website of the Global Union Against Radiation Deployment from Space (GUARDS) at www.stopglobalwifi.org , and the related Cellular Phone Task Force website at www.cellphonetaskforce.org . Both organisations are informed and inspired by the tireless research and campaigning of Arthur Firstenberg, to whom this article is greatly indebted.
Source: ISEE/ISEA Conference: Environmental Epidemiology and Exposure , Paris, 5/9/2006
The rule is, the higher the frequency at which the wave oscillates, the shorter the wavelength will be.
Source: Qualcomm, July 2018
Arno Thielens et al., “Exposure of Insects to Radio-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields from 2 to 120 GHz”, Nature , 8: 3924 (2018): “The insects show a maximum in absorbed radio frequency power at wavelengths that are comparable to their body size… The studied insects that are smaller than 1cm show a peak in absorption at frequencies (above 6 GHz), which are currently not often used for telecommunication, but are planned to be used in the next generation of wireless communication systems.”
Cindy Russell, “A 5G Wireless Future,” The Bulletin (January/February, 2017), pp.20-23, reviews the research, and lists a large number of adverse health effects of millimetre wave electromagnetic radiation including arrythmia, antibiotic resistance, cataracts, compromised immune system, etc.
Source: Arno Thielens et al., Nature , 8: 3924 (2018), fig.4
Kurt Oughstun, interview on “Brillouin Precursors,” Microwave News, 22, 2 (2002), p.10. According to Oughstun, a professor of electrical engineering and mathematics at the University of Vermont, “A single Brillouin precursor can open small channels through the cell membrane because, as it passes through the membrane, it can induce a significant change in electrostatic potential across that membrane.” See also Arthur Firstenberg, “5G – From Blankets to Bullets,” January 17, 2018, at www.cellphonetaskforce.org .
For example, in the ARPANSA fact sheet on “Wi-fi and Health” (“There is no established evidence that the low exposure to RF EME from Wi-fi adversely affects the health of children or the general population”) and on “Mobile Phones and Health” (“There is no established evidence that the use of mobile phones causes any health effects”), for which see www.arpansa.gov.au . Given the vast amount of evidence indicating adverse health effects, one wonders what it takes for this evidence to be “established.”
ARPANSA TSR-164 Report, Review of Radiofrequency Health Effects Research – Scientific Literature 200-2012 (2014). This report has been critiqued by Victor Leach and Steven Weller of the Oceania Radiofrequency Scientific Advisory Association (ORSAA) in Radio Frequency Exposure Risk Assessment and Communication: Critique of ARPANSA TRS-164 Report: Do We Have a Problem? (2017), available at www.orsaa.org. Leach and Weller point out the derivative nature of the ARPANSA report, as well as serious flaws in its assessment of the evidence, which simply does not support the conclusions reached.
Report of the Advisory Group on Non-Ionising Radiation, Health Effects from Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields (2012)
Sarah J. Starkey, “Inaccurate official assessment of radiofrequency safety by the Advisory Group on Non-ionising Radiation,” Review of Environmental Health , 31:4 (2016), pp.493-503
The Australian Government Department of Communication and the Arts, October 2017 strategic report on the roll out of 5G, “5G – Enabling the Future Economy,” does not mention health and safety precautions.
One of the best sources for this mountain of research is The BioInitiative Report (2012), which helpfully gathers it into manageable sections, and is regularly updated. It can be accessed online at www.bioinitiative.org . According to the Report, between 2007 and 2012 approximately 1,800 new studies demonstrated adverse health effects, i.e. on average 350 per year.
Ovum, “5G Economics of Entertainment Report” (October, 2018). The report was commissioned by Intel, and a summary is available at www.newsroom.intel.com
Mark Hertsgaard and Mark Dowie, “The inconvenient truth about cancer and mobile phones,” The Guardian , 14 July 2018. The blatant funding bias was first exposed in 2006 by Louis Slesin, “‘Radiation Research’ and the Cult of Negative Results,” Microwave News , 26.4 (July, 2006), pp.1-5. A good summary of the problem is given in “Bias and Confounding in EMF Science,” on the Powerwatch website: www.powerwatch.org.uk/science/bias.asp
The Interphone Study is devastatingly critiqued in L. Lloyd Morgan et al., Cellphones and Brain Tumors: 15 Reasons for Concern (2009), available online at www.electromagnetichealth.org
Ofcom, Enabling 5G in the UK (March, 2018), pp.3-4
Jacqui Goddard, “Facebook exploits human weakness, admits former boss Sean Parker,” The Times , 10 November 2017
Ovum, “5G Economics of Entertainment Report,” see note 14 above
Maynard Williams, “Welcome to the Internet of Thinking,” The Telegraph , 8 May 2018
Nokia White Paper, “5G – a System of Systems” (www.Nokia.com)
The appeal can be accessed at www.5gspaceappeal.org
Rudolf Steiner, Anthroposophical Leading Thoughts , Rudolf Steiner Press, 2007, p.218
The above article originally appeared in New View magazine (Jan-Feb 2019), and has been modified by the author with information relevant to the Australian situation.